Imagine buying a property in Australia only to find out that recent regulatory changes have significantly altered its value. This scenario is increasingly common as the Australian property market undergoes frequent shifts.
At Unconditional Finance, we focus on offering expert advice and personalised to help our clients navigate the complexities of the property market. Our skilled team stays updated on the latest rules and how they affect property investments, so our clients can make smart choices.
According to CoreLogic, Sydney dwelling values have risen by 14.1% since the market bottomed out, recovering from a 12.4% decline post-January 2022 peak. Experts predict Sydney property values could rise by up to 7% in 2024, despite potential interest rate hikes and economic challenges. Stricter regulatory measures have also decreased foreign property investments, creating a more competitive and less affordable market for international buyers.
This blog explores how recent and upcoming regulatory changes in Australia impact property investors, offering insights and strategies for navigating these changes.
Overview of Regulatory Changes in Australia
Australia’s property market has always been influenced by regulations dating back to early land ownership laws. Over the decades, regulations have evolved to address economic conditions, demographic shifts, and political priorities.
Historical Context and Timeline of Key Regulatory Changes:
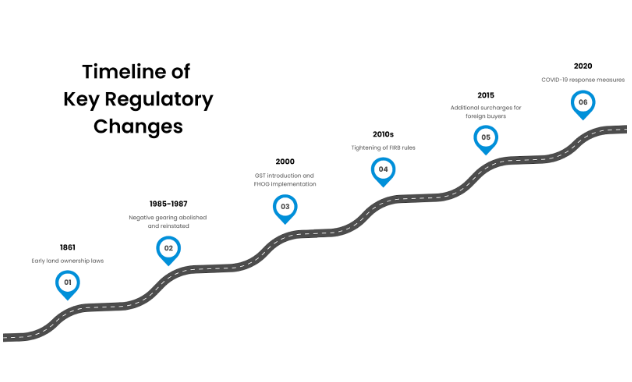
1861: Early Land Ownership Laws (Crown Lands Acts) – The Robertson Land Acts were introduced in New South Wales in 1861. These acts included the Crown Lands Alienation Act and the Crown Lands Occupation Act, designed to allow for the legal purchase and occupation of Crown lands, breaking the monopoly held by squatters and promoting the expansion of the colony.
1910: Introduction of the Land Tax Act – The Land Tax Act was introduced in 1910. This act aimed to tax the unimproved value of land to break up large estates and promote fairer land distribution.
1985: Introduction of the Capital Gains Tax (CGT) – Australia introduced the Capital Gains Tax in 1985 to tax profits from selling assets like property, which were previously tax-free.
1985-1987: Negative Gearing Abolished and Reinstated – Negative gearing was abolished in 1985 by the Hawke government, leading to increased rents and a decline in the rental market. It was reinstated in 1987 to address the issues caused by its abolition.
2000: Introduction of the GST and First Home Owner Grant (FHOG) – The GST was implemented on July 1, 2000, adding a 10% tax on new property purchases. To offset the impact of the GST on home buyers, the First Home Owner Grant (FHOG) was introduced simultaneously to assist first-time buyers.
2010: Tightening of Foreign Investment Review Board (FIRB) Rules – The FIRB rules were progressively tightened, with significant changes made in 2010, to impose restrictions and additional taxes on foreign buyers, ensuring housing availability for Australians.
2015: Additional Surcharges for Foreign Buyers – States like Victoria and New South Wales introduced additional surcharges and taxes for foreign buyers in 2015 to further tighten foreign investment rules and improve housing affordability for local residents.
2020: COVID-19 Response Measures – In 2020, COVID-19 response measures like mortgage relief and rental support were introduced to help those impacted by the pandemic.
In the past 5-10 years, several key regulatory changes have shaped the property investment landscape in Australia:
- Taxation: Tax rule changes, like those to negative gearing and capital gains tax, have greatly affected investment returns.
- Foreign Investment Rules: Stricter rules and additional taxes for foreign buyers aim to ensure housing availability for Australians.
- Zoning Laws: Modifications to zoning laws influence where and what types of properties can be developed, affecting supply and demand dynamics.
Anticipated regulatory changes include further restrictions on foreign investments, potential adjustments to tax policies, and more stringent environmental regulations. These changes could either mitigate or exacerbate current market trends, making it crucial for investors to stay informed.
Impact on Property Investment
Market Dynamics
Regulatory changes can alter market dynamics by influencing both supply and demand. For instance, stricter zoning laws can limit the supply of new properties, driving up prices. Conversely, incentives for first-time homebuyers can increase demand, also pushing up prices.
- Zoning Laws: Changes to zoning laws that restrict development can lead to a decreased supply of new properties. This limited supply can increase property prices as demand remains constant or increases. For example, a new zoning law restricting high-density housing in urban areas can lead to a scarcity of available properties, pushing prices up.
- First-Time Homebuyer Incentives: Government incentives for first-time homebuyers, such as grants and tax breaks, can increase demand for properties. This increased demand, especially in entry-level housing markets, can increase prices and reduce availability for other buyers.
Property Prices
There is a direct correlation between regulation changes and property prices. Taxation adjustments, for example, can either make property investment more attractive or less profitable, thereby influencing market prices. For instance, the tightening of negative gearing laws has cooled investment in some markets, stabilising prices.
- Negative Gearing: Changes to negative gearing laws, such as limiting the ability to deduct rental losses from other income, can reduce the attractiveness of property investment. This reduction can lead to decreased investor demand, stabilising or even lowering property prices in affected markets.
- Capital Gains Tax: Adjustments to capital gains tax can impact both short-term and long-term investors. Short-term investors may be discouraged by higher taxes on quick resale, leading to reduced flipping activity. Long-term investors might also reconsider their strategies if potential after-tax returns significantly decrease.
Investment Strategies
Investors need to adapt their strategies in response to regulatory changes. This could mean diversifying investment portfolios to mitigate risk or focusing on regions with favourable regulations. For example, an investor might pivot to commercial properties if residential property regulations become too restrictive.
- Diversification: By diversifying into different property types (residential, commercial, industrial) and regions, investors can spread their risk. For example, an investor affected by stringent residential regulations in one state might invest in commercial properties in another state with more favourable laws.
- Regulatory Favorability: Focusing on regions with more favourable regulations can help investors maintain profitability. For instance, an investor might shift focus to states offering better tax incentives or less restrictive zoning laws.
Key Regulatory Areas to Watch

Taxation Policies
Changes in taxation policies can have a profound impact on property investment. Key areas to watch include:
- Capital Gains Tax: Adjustments in capital gains tax can influence the profitability of property investments, particularly for long-term investors. For Example, an investor planning to sell a property after 10 years may see a significant increase in CGT liability if the discount is reduced from 50% to 25%, potentially making long-term holding less attractive.
- Stamp Duty: Variations in stamp duty rates can affect the upfront cost of property purchases, impacting affordability and investment decisions. For example, an investor in Melbourne saw their expected rental yield drop by 2% following the new stamp duty regulations, which increased the initial cost of purchasing property.
- Negative Gearing: Changes to negative gearing rules can alter the attractiveness of property investment, as they affect the ability to offset rental losses against other income. For example, tightening negative gearing laws has led to reduced investment activity in some markets, stabilising property prices as fewer investors enter the market.
Foreign Investment Rules
Restrictions on foreign investors can significantly impact the property market. Key considerations include:
- Additional Taxes and Surcharges: Higher taxes and surcharges for foreign investors aim to cool the market and make housing more accessible to locals. For example, the introduction of a 7% foreign purchaser duty and a 1.5% absentee owner surcharge has reduced foreign investment in major cities, leading to a slight cooling of property prices.
- Approval Processes: Stricter approval processes can deter foreign investment, affecting demand and potentially stabilising property prices. For example, foreign investors facing longer approval times and more stringent criteria may look to invest in other countries with more favourable conditions, reducing demand in the local market.
Environmental Regulations
Sustainability and green building regulations are becoming increasingly important in property development and investment. Key points include:
- Green Building Standards: Compliance with green building standards can increase construction costs but also enhance property value and appeal. For example, implementing energy-efficient designs and materials can raise initial construction costs by 5-10%, but properties meeting these standards often have higher market values and lower long-term operational costs.
- Energy Efficiency Requirements: Regulations aimed at improving energy efficiency can lead to higher initial investments but lower long-term operational costs. For example, investors developing properties with energy-efficient features may incur higher upfront costs but benefit from reduced energy expenses and increased tenant demand due to lower utility bills.
Housing Affordability Measures
Government initiatives to improve housing affordability can have diverse impacts on investors. Key measures include:
- First Home Buyer Grants: Grants and incentives for first-time homebuyers can boost demand in certain segments of the market. For example, the First Home Owner Grant (FHOG) has increased demand for entry-level properties, driving up prices in certain areas and creating opportunities for investors to cater to this market.
- Affordable Housing Programs: Programs aimed at increasing the supply of affordable housing can influence market dynamics and rental yields. For example, Government programs to develop affordable housing units can increase the supply of rental properties, potentially stabilising rental yields as more affordable options become available.
Actionable Advice for Property Investors
Staying Informed
To stay ahead of regulatory changes, investors should:
- Subscribe to Newsletters: Regular updates from industry experts and regulatory bodies can provide valuable insights.
- Attend Seminars and Workshops: Engaging with Sydney mortgage brokers at seminars and workshops helps in understanding the latest trends and regulations.
Risk Management
Mitigating risks associated with regulatory changes involves:
- Regular Reviews: Periodically review investment portfolios to assess regulatory impacts and adjust strategies accordingly.
- Contingency Planning: Making contingency plans to address potential adverse regulatory changes.
Diversification
Diversifying investments can safeguard against regulatory risks by:
- Investing in Different Regions: Spreading investments across various regions with differing regulatory environments can reduce risk exposure.
- Diversifying Asset Types: Including a mix of residential, commercial, and industrial properties can balance risk and return.
Professional Guidance
Seeking advice from property experts and legal professionals is crucial. Considerations include:
- When to Seek Advice: Engaging professionals when planning significant investments or when facing complex regulatory environments.
- How to Choose Experts: Selecting reputable and experienced professionals with a thorough understanding of property regulations.
Conclusion
Regulatory changes in taxation policies, foreign investment rules, environmental regulations, and housing affordability measures significantly impact property investment in Australia. Staying informed and adaptable is vital for property investors to navigate the evolving regulatory landscape successfully.
How have regulatory changes affected your property investments? Tell us about your experiences in the comments or contact our expert team for personalised advice.
FAQs
- What are the major regulatory changes affecting property investment in Australia? Major changes include adjustments to negative gearing, capital gains tax, foreign investment rules, and zoning laws.
- How does negative gearing impact property investors? Negative gearing allows investors to deduct rental losses against other income, reducing taxable income. Changes can affect profitability and investment attractiveness.
- What are the recent changes in foreign investment rules in Australia? Recent changes include tighter restrictions and additional taxes aimed at ensuring housing availability for Australians and cooling the property market.
- How have zoning laws changed in Australia? Changes in zoning laws can restrict or enable property development, impacting supply and demand dynamics and influencing property prices.
- What impact does the Goods and Services Tax (GST) have on property purchases? The GST adds a 10% tax on new property purchases, affecting affordability and overall market activity.
- How do government incentives for first-time homebuyers affect the property market? Incentives such as grants and tax breaks increase demand for entry-level properties, driving up prices and reducing availability for other buyers.
- What measures were introduced in response to the COVID-19 pandemic? The pandemic measures, such as mortgage relief and rent support, helped people and businesses, which temporarily changed the market.
- How do environmental regulations impact property investment? Compliance with green building standards and energy efficiency requirements can increase initial costs but enhance property value and appeal over time.
- What should investors do to stay informed about regulatory changes? To keep up with the latest regulatory trends and changes, investors should read newsletters, go to seminars, and talk to industry experts.
- How can diversification help mitigate risks associated with regulatory changes? Diversifying investments across different regions and property types can reduce exposure to regulatory risks and balance potential returns.