When it comes to securing a home loan, Australian homebuyers have various choices. The two primary options are big banks and second-tier lenders. Each has pros and cons, so knowing the differences is essential to make a smart decision. In this blog, we’ll explore the key factors to consider when choosing between big banks and second-tier lenders for your home loan, helping you find the best fit for your financial situation and goals.
What Are Big Banks and 2nd Tier Lenders?
Big Banks are the primary, well-known financial organisations that provide various banking services, including house loans. Examples in Australia include Commonwealth Bank, Westpac, ANZ, and NAB. These banks have extensive networks, comprehensive service offerings, and a long-standing presence in the market.
2nd Tier Lenders are smaller financial institutions, often specialising in home loans and personal banking. These lenders include credit unions, building societies, and specialised mortgage companies like ING Direct, Bankwest, and Bendigo Bank. They often provide competitive rates and more personalised service.
APRA (Australian Prudential Regulation Authority)
APRA is the regulatory body overseeing financial institutions in Australia, including banks, credit unions, and insurance companies. It ensures the financial system’s stability by enforcing stringent standards and practices, safeguarding deposits, and maintaining public confidence in the financial system.
Differences from Big Banks
- Regulation: 2nd-tier lenders are also regulated by APRA (Australian Prudential Regulation Authority), ensuring they meet strict financial and operational standards.
- Market Share: They hold a smaller market share compared to the big banks but are growing in popularity due to their customer-focused approach.
Big Banks’ Interest Rates
Big banks typically offer a range of interest rates based on the type of loan, the loan amount, and the borrower’s credit profile. As of 2023, the interest rates from the Big 4 banks (Commonwealth Bank, Westpac, ANZ, NAB) are generally higher than those from 2nd tier lenders, reflecting their extensive service offerings and operational costs.
Leading Mortgage Lenders in Australia in 2023
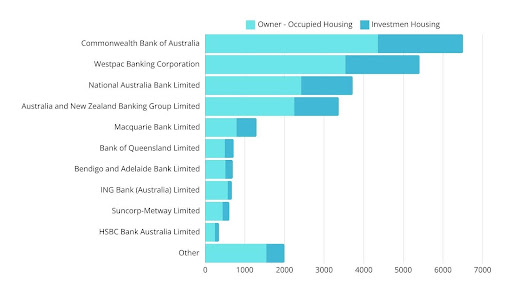
Source: Statista
According to recent data, the leading mortgage lenders in Australia by the value of gross lending include:
Commonwealth Bank of Australia (CBA)
- Total Gross Lending: AUD 6,506.56 billion
- Market Position: The largest mortgage lender in Australia.
- Key Strengths: Broad branch network coverage, sophisticated online banking capabilities, and an extensive selection of financial products.
- Focus Areas: Strong emphasis on both owner-occupied and investment housing.
- Technological Edge: Known for investing heavily in technology, providing customers with robust digital banking solutions.
Westpac Banking Corporation
- Total Gross Lending: AUD 5,411.72 billion
- Market Position: One of the “Big Four” banks in Australia.
- Key Strengths: Comprehensive service offerings, extensive ATM and branch networks, and a strong focus on customer service.
- Focus Areas: Balanced lending portfolio between owner-occupied and investment housing.
- Innovations: Continuously developing online and mobile banking platforms to enhance customer experience.
Australia and New Zealand Banking Group Limited (ANZ)
- Total Gross Lending: AUD 3,372.03 billion
- Market Position: One of the top four banks in Australia with a significant presence in the Asia-Pacific region.
- Key Strengths: Diverse range of financial services, strong international presence, and robust risk management practices.
- Focus Areas: Equally focused on both owner-occupied and investment housing loans.
- Customer Service: Known for providing tailored financial solutions to meet diverse customer needs.
National Australia Bank Limited (NAB)
- Total Gross Lending: AUD 3,722.83 billion
- Market Position: Another major player among the “Big Four” banks.
- Key Strengths: Comprehensive range of banking and financial services, strong customer service, and extensive branch network.
- Focus Areas: Offers a balanced mix of loans for owner-occupied and investment housing.
- Community Involvement: Actively involved in community initiatives and sustainability programs.
Macquarie Bank Limited
- Total Gross Lending: AUD 1,296.66 billion
- Market Position: Leading investment bank with a growing presence in retail banking.
- Key Strengths: Strong in investment housing loans, flexible financial solutions, and personalised service.
- Focus Areas: Predominantly focused on investment housing with innovative financial products.
- Innovation: Known for its innovative approach to financial services and wealth management.
Bank of Queensland Limited (BOQ)
- Total Gross Lending: AUD 719.48 billion
- Market Position: Prominent regional bank with a strong customer base in Queensland.
- Key Strengths: Personalised banking services, strong regional presence, and competitive loan products.
- Focus Areas: Emphasis on owner-occupied housing loans.
- Customer Service: Renowned for its customer-centric approach and community involvement.
Bendigo and Adelaide Bank Limited
- Total Gross Lending: AUD 696.22 billion
- Market Position: Major regional bank with a strong focus on community banking.
- Key Strengths: Personalised service, strong community ties, and competitive loan offerings.
- Focus Areas: Balanced lending portfolio between owner-occupied and investment housing.
- Sustainability: Actively promotes sustainable and ethical banking practices.
ING Bank (Australia) Limited
- Total Gross Lending: AUD 673.5 billion
- Market Position: Well-known for its direct banking model with no branch network.
- Key Strengths: Competitive interest rates, strong online banking platform, and customer satisfaction.
- Focus Areas: Focus on owner-occupied housing loans.
- Digital Leadership: Leading in digital banking solutions and innovative financial products.
Suncorp-Metway Limited
- Total Gross Lending: AUD 611.4 billion
- Market Position: Diversified financial services group with a strong presence in Queensland.
- Key Strengths: Comprehensive range of banking, insurance, and wealth management services.
- Focus Areas: Provides a mix of loans for both owner-occupied and investment housing.
- Customer Experience: Known for its focus on delivering exceptional customer service and community support.
HSBC Bank Australia Limited
- Total Gross Lending: AUD 348.34 billion
- Market Position: Part of the global HSBC Group, with a strong presence in international banking.
- Key Strengths: Expertise in international banking, strong global network, and competitive mortgage products.
- Focus Areas: Balanced focus on owner-occupied and investment housing loans.
- Global Reach: Leverages its global network to offer unique financial solutions to expatriates and international clients.
Pros and Cons of Big Banks
Pros
- Reputation and Stability: Big banks have established reputations and are seen as stable and secure, providing peace of mind for borrowers.
- Comprehensive Services: They provide a wide range of financial products and services, making it simple to meet multiple financial needs in one location.
- Extensive Branch and ATM Networks: With numerous branches and ATMs nationwide, accessing services is usually more convenient.
- Advanced Technology: Big banks typically invest heavily in technology, offering robust online banking platforms and mobile apps. These tools can make managing your loan and other financial products more straightforward and efficient.
Cons
- Higher Fees and Interest Rates: Big banks often charge higher fees and interest rates than 2nd-tier lenders.
- Less Personalised Service: Due to their size, the customer service experience can be less personalised and more bureaucratic.
- Strict Lending Criteria: They have more rigorous lending standards, making it more difficult for some borrowers to qualify for loans.
Pros and Cons of 2nd Tier Lenders
Pros
- Competitive Rates and Fees: 2nd-tier lenders often offer lower interest rates and fees, making home loans more affordable.
- Personalised Service: These lenders typically provide a more personalised service, focusing on building customer relationships.
- Flexible Lending Criteria: They may have more flexible lending criteria, which can benefit borrowers with unique financial situations.
- Innovative Products: 2nd-tier lenders often offer innovative loan products tailored to borrowers’ needs. This innovation can provide more options and customised solutions for different financial circumstances.
Cons
- Limited Branch and ATM Networks: These networks generally have fewer physical locations, which can be less convenient for some customers.
- Less Diverse Product Range: While they may excel in home loans, their range of other financial products might be more limited.
- Perceived Risk: Some borrowers may perceive 2nd-tier lenders as less stable than big banks, although many are highly reputable and secure.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Big Banks and 2nd Tier Lenders
Interest Rates and Fees: Comparing the interest rates and fees of various lenders. Even slight differences in interest rates can influence the overall cost of your loan over time. Additionally, watch out for hidden fees that might affect your budget.
Loan Features and Flexibility: Look at each lender’s offerings, such as offset accounts, redraw facilities, and flexible repayment options. Consider which features are essential for your financial strategy.
Customer Service and Support: Assess the level of customer service you need. If you prefer a more personal touch, a 2nd tier lender might be more suitable. Excellent customer service can make managing your loan a smoother experience.
Approval Times: Consider the approval times for home loans. Some lenders may provide faster approval processes, which can be critical in a competitive real estate market. Quick approvals can give you an edge when bidding on your dream home.
Financial Stability and Security: Evaluate the lender’s financial stability and security. Big banks often provide more reassurance in this area, but many 2nd tier lenders are also financially sound.
Technology and Accessibility: If you value advanced online banking tools and easy access to your accounts, the technological offerings of each lender can be a deciding factor. Efficient technology can enhance your banking experience and save you time.
Choosing between a big bank and a 2nd-tier lender for your home loan is an important decision determined by your circumstances, financial goals, and preferences. Big banks offer stability, comprehensive services, and extensive networks, while 2nd-tier lenders provide competitive rates, personalised service, and flexible lending criteria. By carefully weighing the advantages and disadvantages of each option and examining important factors such as interest rates, loan features, and customer service, you will be able to make an informed choice that suits your requirements best.
Still unsure whether to choose a big bank or a 2nd tier lender? Get in touch with our mortgage experts for personalised advice and start your home-buying journey with confidence!